How to clean and maintain stainless steel?

Stainless steel is a popular and commonly used material for producing equipment for public toilets. Metal liquid soap dispensers, paper towel dispensers, toilet paper holders, trash cans, toilet brushes, sinks, toilet bowls, grab bars for disabled, and other bathroom accessories can be found in many public restrooms. We advise on how to properly maintain stainless steel so that objects made from it last long and look aesthetically pleasing. Improper cleaning can cause discoloration and corrosion on the surface of stainless steel objects.
Table of Contents
Types of stainless steel
Stainless steel is commonly referred to as "stainless". The term stainless steel encompasses types of steel with a high degree of purity, produced using special technology. The concentration of alloying elements and thus the type of steel is determined by standards such as American AISI, German DIN, or European EN 10088. For the purposes of this article, we will use the widely used AISI standard. The most commonly used types of stainless steel for sanitary equipment production are:
- AISI 430, also known as chrome steel:
- good corrosion resistance
- very hard
- smooth surface, easy to clean
- magnetic
- AISI 304, also known as chrome-nickel steel V2A
- good corrosion resistance
- 8-10% nickel content increases corrosion resistance
- non-magnetic
- AISI 316L, also known as chrome-nickel-molybdenum steel V4A
- very good corrosion resistance
- the addition of molybdenum in V4A significantly increases corrosion resistance, making it recommended for environments with high levels of sulfur oxides and chlorides
- non-magnetic
Properties of stainless steel, or why it is used for WC equipment production
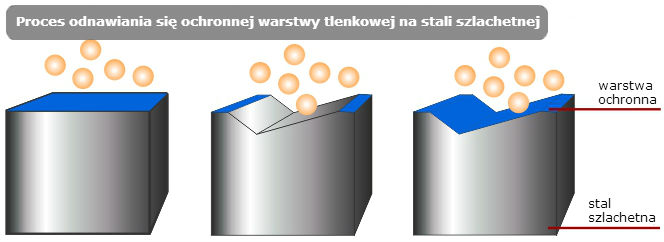
- resistant to corrosion - there is a very thin oxide layer on the surface of steel, which prevents corrosion; it regenerates itself under the influence of oxygen from the air or water and naturally creates a protective coating
- hygienic - without pores, the smooth surface is easy to clean and disinfect
- shows high tolerance to high temperatures and temperature fluctuations
- durable - resistant to mechanical damage and impacts
- environmentally friendly - steel products can be melted down and fully reused (50% of products come from recycled waste)
- cost-effective - steel products are more expensive than plastic ones, but they are more durable and last longer, making them a cheaper solution in the long run
- gives rooms an elegant character

Causes of stainless steel corrosion. Why is cleaning steel so important?
What to use for cleaning noble steel?
You can use the following for cleaning steel:
- household cleaning products household chemicals
- natural products, such as a solution of vinegar (20% vinegar, 80% water) or baking soda (2 tablespoons per liter of warm water)
- water with liquid soap
- window cleaning fluids - most of them are safe for steel
- products for cleaning and shining steel.
Excellent materials for cleaning are:
- brushes with natural and synthetic bristles
- microfiber cloths, chemical and natural fibers
- non-woven fabrics made of synthetic materials
- sponge cloths, sponges
- pressure washers and steam cleaners.
What should not be used to clean stainless steel?
- steel wool
- sandpaper
- rough scrubbers
- abrasive powders for scrubbing, sanding, and polishing, etc.
Most common stains on stainless steel and methods for removing them
When discolorations appear on the surface of stainless steel objects (waste bins, soap dispensers, toilet brushes, etc.), the first step should be to clean them with an appropriate product. Depending on the type of stain, different products should be used.
| Type of dirt | Methods of removal | Notes |
| Stains resembling rust | Wipe the surface with a cloth and water and soap, rinse with running water and dry thoroughly; use gentle cleaning agents and regularly clean and dry steel surfaces | Commonly encountered, mainly due to washing steel with improper agents, splashing with urine or substances containing reactive components; occur on the surfaces of equipment, while the interiors and edges are usually free from stains |
| Rust | Use acidic agents with a low pH, rinse with cold water and dry | Acidic agents can also be used to remove limescale deposits |
| Fingerprints | Remove using window cleaner or by using alcohol or a cloth soaked in a mild detergent; then rinse with cold water and dry | As mentioned before, most window cleaners are suitable for cleaning steel |
| oils, greases, fats | clean with an organic solvent, then wipe with warm water and soap or a gentle cleaning agent, rinse with clean water and dry | |
| paint | wipe with a paint solvent, wash with clean water and dry | |
| stubborn stains, discoloration and temperature deposits | clean with a detergent, rinse with cold water and dry | if it is brushed steel, remove stains by cleaning in the direction of the brushing structure |
| scratches | gently sand with a non-iron wool (without adding iron) in the direction of the original sanding, wash with a mild cleaning agent and then clean water, dry | before removing scratches, it is worth doing a test in an invisible place; sand in the direction of the brushing structure |
Tips for caring for stainless steel
| Problem | Tip |
| Cleaning equipment made of satin stainless steel (matte, brushed) | clean in the direction of brushing to avoid damaging the structure |
| Lime deposits and streaks | always wipe dry after cleaning steel surfaces |
| Dust and particles on equipment | use non-abrasive and non-dusting cloths that do not leave particles on the cleaned surfaces; microfiber cloths are a good solution |
| Despite regular cleaning, discoloration or rust appears on steel equipment | check if we are using the appropriate cleaning agent, and if so, increase the frequency of cleaning to remove unwanted deposits |
| Stainless steel appliances are meant to maintain their appearance for a long time | purchase products for caring for stainless steel; they create additional thin protective layers that, when used with gentle cleaning agents, can last on steel surfaces from a few days to even a few weeks, depending on the intensity of use |
Ryszard Kurek
All rights reserved. No part of the publication (text, graphics, images, photos, files, and other data) presented in the OLE.PL online store may be reproduced or distributed in any form or by any means without prior permission. All trademarks, graphics, brand names, and other data are protected by copyright and belong to their respective owners.











































































 Polski
Polski
 Czech
Czech
 German
German
 Spanish
Spanish
 Slovak
Slovak